The global precision firearms market has undergone a radical transformation over the last fifteen years, shifting from modified sporting actions and traditional wood-stock architectures to purpose-built, chassis-based systems capable of extreme long-range (ELR) interdiction. Within this hyper-competitive landscape, Victrix Armaments, an Italian manufacturer with deep roots in high-precision aerospace and medical machining, has established the Tormentum series as a flagship offering in the heavy-caliber segment. Designed specifically for the .375 and .408 CheyTac cartridges, the Tormentum represents a fusion of traditional European gunsmithing tolerances with modern CNC manufacturing and advanced materials science.1
This comprehensive research report provides an exhaustive engineering and market analysis of the Victrix Tormentum. It evaluates the system’s design philosophy, metallurgical composition, operational performance, and standing within the broader ELR ecosystem. The analysis is driven by a synthesis of technical datasheets, competitive benchmarking, independent field reports, and verified performance records from global competitions such as the “King of 2 Miles” (KO2M).
Our findings indicate that the Tormentum occupies a unique “ultra-premium” niche. It is positioned not merely as a tool, but as a precision instrument that prioritizes ballistic superiority and aesthetic perfection over the utilitarian roughness often found in standard-issue military hardware. The core of the system—the Marte CT action—features a distinct asymmetrical three-lug bolt design (105°/105°/150°) machined from AISI 630 stainless steel, a material choice that underscores the manufacturer’s commitment to structural integrity under the immense pressures of CheyTac ignition.1
However, this pursuit of engineering perfection introduces specific operational considerations. Analyst feedback and customer sentiment data reveal that the Tormentum’s tight, match-grade tolerances require a higher degree of operator care and ammunition consistency than some of its looser, more combat-oriented competitors.4 While its performance in controlled environments and ELR competitions is peerless—demonstrated by recent podium finishes at KO2M—its adoption in broad-spectrum military applications remains targeted toward specialized units rather than general infantry deployment.6
This report serves as a definitive technical dossier for defense procurement officers, industry investors, and high-level competitive shooters, offering a granular Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis and a nuanced verdict on the platform’s strategic value.
1.0 Strategic Context and Corporate Lineage
To fully appreciate the engineering nuances of the Tormentum, one must first analyze the pedigree of Victrix Armaments. Unlike legacy manufacturers with centuries of history, Victrix is a relatively young entity that was born out of the Lombardy region’s precision machining sector, a hub of European metallurgy and industrial craftsmanship.
1.1 Origins of Victrix Armaments: The Foundation of Precision
Victrix Armaments was founded in 2014, but its roots extend deeper into the operations of Rottigni Officina Meccanica, a high-tech machining company located near Bergamo, Italy.6 For decades, Rottigni served as a strategic partner and component manufacturer for various industries requiring extreme tolerances, including the medical and aerospace sectors. This background is critical to understanding the Victrix ethos: the company approaches firearm manufacturing not from a traditional gunsmithing perspective, but from the standpoint of precision industrial engineering.
The transition from component supplier to a standalone firearms brand was driven by a desire to produce a “no-compromise” rifle system. Giuseppe Valtorta, the founder and CEO, leveraged the company’s advanced CNC capabilities to design actions and chassis systems that adhered to tolerances previously reserved for custom benchrest rifles, applying them to tactical platforms.8 This “Anima” (Soul) philosophy, as marketed by the company, emphasizes the connection between the shooter and the machine, treating the rifle as a biomechanical extension of the operator.9
1.2 The Beretta Holding Era: Acquisition and Integration
A pivotal moment in the company’s history occurred in late 2016 when Beretta Holding, the oldest firearms manufacturer in the world, acquired the Victrix brand.3 This acquisition was strategic for both parties. For Beretta, it filled a crucial gap in their defense portfolio (Beretta Defense Technologies or BDT), specifically in the realm of specialized sniper rifles where their existing Sako TRG line, while excellent, did not fully cover the niche of heavy-caliber ELR interdiction in the same manner as the Tormentum.10
For Victrix, the acquisition provided an infusion of capital and, more importantly, access to Beretta’s massive global distribution network and military contracting channels. During this period, Victrix rifles were marketed alongside Sako, Tikka, and Steiner optics, benefiting from the logistical support of a global defense giant. The collaboration allowed Victrix to refine its production processes, adopting “lean manufacturing” techniques and automated surface treatment plants located in Beretta’s Gardone Val Trompia facilities.10 This era solidified the brand’s reputation for quality control and operational capability.
1.3 Return to Independence: The 2024 Restructuring
The corporate narrative took another significant turn in recent years. As of March 2024, Victrix Armaments announced a strategic restructuring that saw it regain distribution rights for the Military and Law Enforcement (LE) sectors, effectively separating these operations from the exclusive control of Beretta Defense Technologies.6 This move to re-acquire independence signals a shift back to the agility of a boutique manufacturer.
While the partnership with Beretta provided stability, the return to independence allows Victrix to respond more rapidly to the specialized needs of elite units and civilian competitors without the bureaucratic overhead of a massive conglomerate. It suggests a renewed focus on their core competency: building small batches of extremely high-performance rifles for discerning clients. The rebranding of Rottigni Officina Meccanica solely under the Victrix Armaments name further unifies the design, production, and distribution arms under a single corporate identity, ensuring total control over the product lifecycle.6
1.4 The Minerva Series Philosophy
The Tormentum is the heavyweight anchor of the Minerva series, Victrix’s dedicated product line for tactical and military application.11 The Minerva philosophy is distinct from the company’s Victoria (sporting) and Lunae (hunting) lines.
- Tactical Focus: The Minerva line prioritizes ruggedization, modularity, and field serviceability. These rifles are finished in non-reflective PVD coatings and hard anodizing, designed to withstand the rigors of operational deployment.12
- The Family of Systems: The series is designed as a scalable family.
- Pugio: A compact urban sniper system in.308 Winchester.11
- Gladio: An intermediate capability in.338 Lapua Magnum and.300 Norma Magnum.3
- Scorpio: A versatile platform often bridging gaps in caliber offerings.
- Tormentum: The extreme long-range specialist in .375 and .408 CheyTac.11
This commonality in ergonomics and manual of arms across the series allows military units to train operators on a smaller caliber platform (like the Pugio) and seamlessly transition them to the heavy Tormentum for anti-material or ELR missions, significantly reducing training overhead.13
2.0 Engineering Anatomy: The Tormentum Platform
The Victrix Tormentum is not merely a scaled-up hunting rifle; it is a clean-sheet design engineered specifically to handle the immense pressures and recoil impulses of the CheyTac cartridge family. The engineering choices reflect a priority on structural rigidity and harmonic consistency.
2.1 The Marte CT Action: A Metallurgical Deep Dive
The heart of the Tormentum is the Marte CT action. In an industry where many manufacturers rely on the ubiquitous Remington 700 footprint (using 4140 Chromoly steel), Victrix differentiates itself through material selection and manufacturing methodology.
- Material Selection: The action is machined from AISI 630 (17-4 PH) stainless steel.1 This precipitation-hardening martensitic stainless steel offers a superior combination of high strength, corrosion resistance, and fracture toughness compared to standard carbon steels. 17-4 PH is widely used in aerospace applications for components requiring high fatigue strength—a critical attribute for a rifle receiver that must endure the repetitive shock of 60,000+ PSI operational pressures.
- Billet Machining: Unlike mass-produced receivers that may be cast or forged near-net-shape and then finished, the Marte action is milled directly from a solid billet. This ensures the integrity of the grain structure and allows for precise control over dimensional tolerances.1
- Surface Treatment: The entire action and bolt assembly undergo Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating.3 PVD is a vacuum deposition method used to produce thin films and coatings. In the context of the Tormentum, this coating provides two critical benefits:
- Extreme Surface Hardness: It significantly increases resistance to wear and scratching, far exceeding traditional bluing or even Parkerizing.
- Inherent Lubricity: The coating reduces the coefficient of friction between moving parts. This allows the action to cycle smoothly with minimal liquid lubrication, which is a major operational advantage in desert environments where oil attracts sand and dust.3
2.2 Bolt Geometry and Fluid Dynamics
The bolt design of the Marte CT action is a significant departure from convention and represents a specific engineering solution to the challenges of ELR ballistics.
- Asymmetrical Lug Spacing: While many tactical rifles use a standard two-lug or symmetrical three-lug (120° spacing) design, the Victrix Marte bolt utilizes a three-lug design with asymmetrical spacing: 105°, 105°, and 150°.1
- Engineering Rationale:
- Feeding Reliability: The 150° gap is positioned at the bottom (6 o’clock) when the bolt is open. This wider gap provides greater clearance for the cartridge to rise from the magazine, improving feeding geometry and reducing the risk of jams with the large, heavy CheyTac rounds.15
- Harmonic Stabilization: Victrix claims this spacing is optimized to resist the specific harmonic flexing and vibrations caused by firing. By altering the support points of the bolt head, the design minimizes the “whip” or deflection of the action during the millisecond of peak pressure, contributing to consistent lock-up and, consequently, better accuracy.3
- Lock Time: The three-lug design necessitates only a 60-degree bolt lift to unlock (as opposed to 90 degrees for a two-lug system). This shorter throw allows for faster cycling and creates more clearance between the bolt handle and the large objective lenses of extreme-range optics.
2.3 Barrel Technology and Harmonics
The barrel is the primary determinant of a rifle’s intrinsic accuracy. Victrix partners with premium barrel manufacturers (historically Benchmark, though they now produce many components in-house) to spec barrels that meet their stringent requirements.
- Material: The barrels are manufactured from AISI 416R Match-Grade Stainless Steel.16 416R is a pre-hardened chromium stainless steel specifically designed for precision barrels. It possesses excellent machinability, allowing for incredibly consistent bore dimensions and rifling cuts, and high tensile strength to withstand the hoop stress of firing.
- Dimensions: The standard barrel length for the Tormentum is 30 inches (762mm).14 In the world of .375 CheyTac, barrel length is horsepower. The large powder columns (often 130-140 grains of slow-burning powder) require significant bore volume to achieve a complete burn and maximize velocity. A shorter barrel would result in unburnt powder and reduced velocity, severely handicapping the cartridge’s long-range potential.
- Contour and Fluting: The barrels feature a heavy match contour to act as a heat sink and provide rigidity. To offset the weight, they are deeply fluted. This fluting increases the surface area for convective cooling and reduces the overall mass of the barrel without compromising its stiffness as much as reducing the diameter would.1
- Rifling Twist Rates:
- .375 CheyTac: 1:10″ twist.11 This fast twist is necessary to stabilize the long, heavy high-BC (Ballistic Coefficient) solids typically weighing between 350 and 400 grains.
- .408 CheyTac: 1:13″ twist.11 This is optimized for the standard 419-grain solid projectiles synonymous with the caliber.
2.4 Chassis System and Human Factors Engineering
The “Minerva” chassis is not just a stock; it is a modular aluminum interface designed to adapt the rifle to the shooter and isolate the operator from the recoil.
- Materials: The chassis is machined from aluminum alloy and hard anodized for scratch resistance.18 The choice of aluminum provides a rigid bedding platform that is impervious to humidity and temperature shifts, unlike wood or some composites.
- The Folding Evo Stock: Transporting a rifle with a 30-inch barrel is a logistical challenge. The Tormentum addresses this with a side-folding stock mechanism. The overall length of the rifle is approximately 57-60 inches deployed, but the stock folds to reduce this to roughly 48 inches, allowing it to fit into standard Pelican-style hard cases or vehicle racks.14 The folding hinge is a critical stress point; Victrix uses a robust locking mechanism to ensure zero play when deployed.
- Ergonomic Adjustability: The “Advanced Buttstock” is fully adjustable.
- Length of Pull (LOP): Adjustable via lever or tool-less mechanism, typically with a 50mm range.16
- Cheek Riser: Vertically adjustable (60mm range) to align the shooter’s eye with large-objective optics mounted on high rings.16 Importantly, the cheek piece is made of an insulated material, preventing the shooter’s face from freezing to the metal in cold environments or burning in the heat—a small but vital detail for operational comfort.1
- Integrated Support: A retractable monopod is integrated into the rear of the stock. It features both a quick-deploy coarse adjustment and a fine-threaded adjustment wheel for precise elevation control.1 This “third leg” provides the stability of a benchrest in the field, essential for the extended observation periods common in sniper operations.
- Forend Interface: The forend utilizes an Octagonal Elliptic shape, which is ergonomic for hand-holding and provides a flat bottom for resting on barricades. It features M-LOK slots (or proprietary interfaces on earlier models) for mounting accessories like rangefinders, night vision illuminators, or tripod adapters.14
- Carry Handle: A dedicated, multi-function carry handle is attached to the chassis. Given the rifle’s weight (approx. 11.5kg / 28lbs), carrying it by the scope or sling alone is impractical. The handle is positioned at the center of gravity. It also serves as a mounting point for accessories and includes a magnetic bit holder with field tools, allowing the operator to perform maintenance without carrying a separate toolkit.1
3.0 Ballistic Capability and Cartridge Integration
The operational envelope of the Tormentum is defined by the cartridges it chambers. The .375 and .408 CheyTac are specialized rounds designed to dominate the “intermediate” zone between.338 Lapua Magnum and .50 BMG (12.7x99mm).
3.1 The .375 CheyTac: The King of ELR
While the Tormentum is available in both calibers, the .375 CheyTac has emerged as the superior choice for extreme long-range precision, largely superseding the .408 in competitive circles.
- Ballistics: The .375 CheyTac is essentially a .408 CheyTac case necked down to accept a .375 caliber bullet. This combination allows the round to fire a slightly lighter, more aerodynamic projectile at higher velocities.
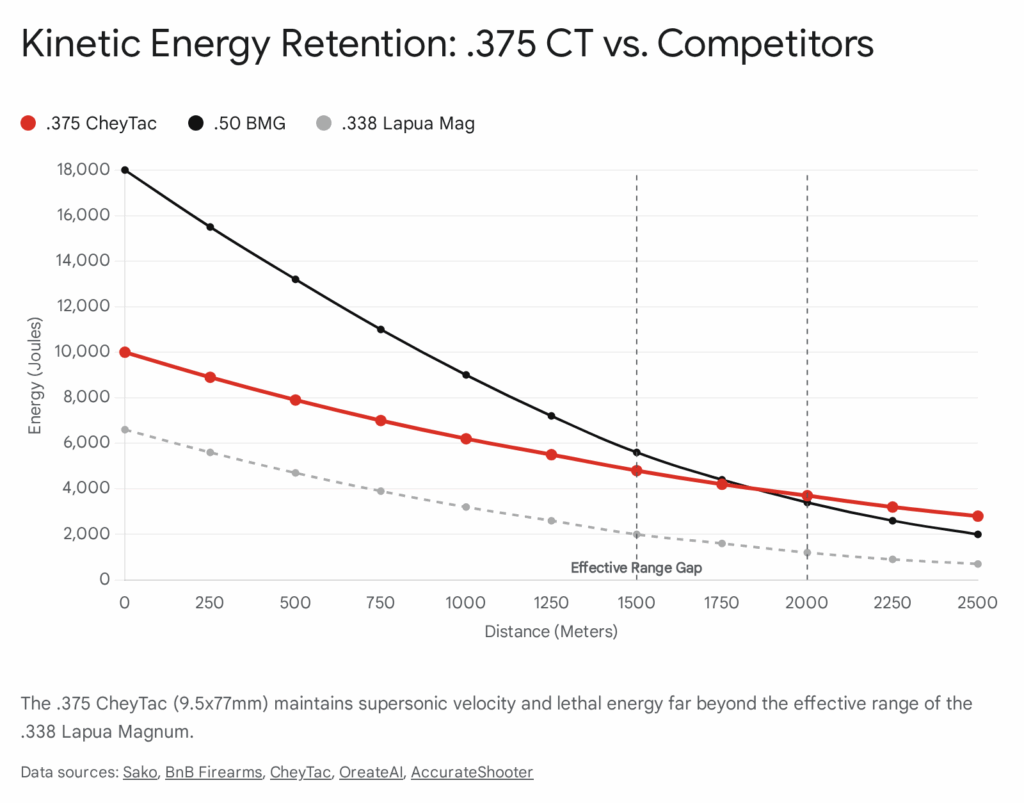
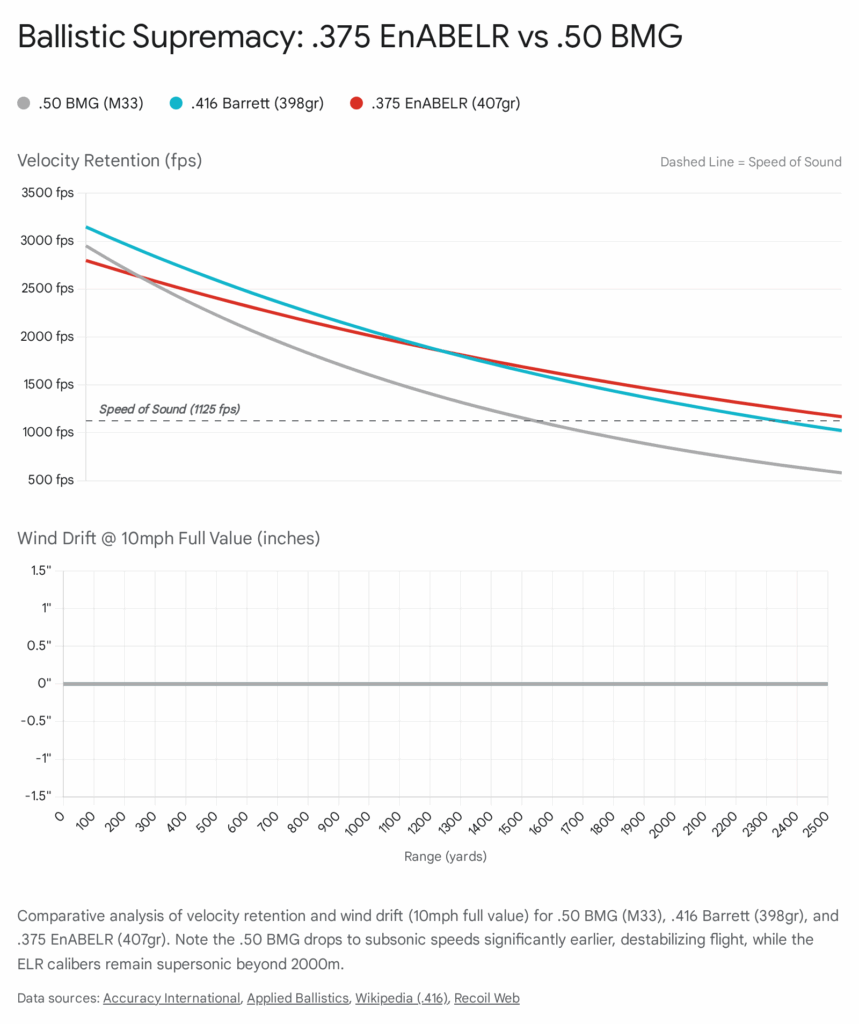
- Supersonic Range: Modern solid projectiles (lathe-turned monometals from manufacturers like Cutting Edge or Warner Tool Company) in .375 often boast Ballistic Coefficients (G1) exceeding 1.0. This allows the projectile to remain supersonic—and thus stable and predictable—beyond 2,500 meters.19
- Trajectory: Compared to the .408, the .375 offers a flatter trajectory, meaning there is less bullet drop at any given distance. This reduces the margin of error for range estimation, increasing the hit probability on targets at unknown distances.
3.2 The .408 CheyTac: Anti-Materiel Legacy
The .408 CheyTac remains a formidable option, particularly for military applications where kinetic energy delivery is paramount.
- Energy: The .408 fires a heavier projectile (typically 419 grains), delivering massive kinetic energy (often exceeding 11,000 Joules at the muzzle).20 This makes it more effective for anti-materiel roles, such as disabling radar dishes, light vehicles, or communications equipment at standoff distances.
- The Transition: Despite its energy, the .408 generally has a lower ballistic coefficient than the sleekest .375 projectiles, meaning it bleeds velocity faster. For pure target interdiction at 2+ miles, the .375 is the mathematical winner, which is why most civilian Tormentum sales favor the smaller bore.
3.3 Internal Ballistics and Pressure Management
Managing the internal ballistics of these rounds is a challenge.
- Pressure: The CheyTac family operates at high pressures (approx. 63,000+ PSI / 440 MPa).20 The Marte action’s rigid lock-up is critical here.
- Recoil Impulse: The recoil generated is significant. The Tormentum mitigates this through:
- System Mass: At 11.5 kg (25.35 lbs), the rifle’s inertia absorbs a large portion of the recoil energy.1
- Muzzle Brake Efficiency: The standard Victrix ProAngle brake uses three forward-canted chambers to redirect high-pressure gas rearward and upward. This reactive force pulls the rifle forward, counteracting the recoil, and pushes the muzzle down, fighting muzzle rise.1
- The Magnus Brake: Victrix has also introduced the “Magnus” brake, an advanced design claimed to reduce gas turbulence around the bullet by 96% and sound pressure by 12dB. By strictly controlling the laminar flow of gas as the bullet exits, it minimizes the “yaw” induced by gas blow-by, further enhancing accuracy.21
Table 1: Technical Specification Comparison ( .375 vs .408 Variants)
| Feature | Tormentum .375 CheyTac | Tormentum .408 CheyTac |
| Twist Rate | 1:10″ | 1:13″ |
| Typical Bullet Weight | 350 – 400 gr | 400 – 420 gr |
| Muzzle Velocity (Approx) | 2,850 – 3,050 fps | 2,900 – 3,000 fps |
| Effective Range (Supersonic) | ~2,500m+ | ~2,200m+ |
| Primary Use Case | ELR Competition / Anti-Personnel | Anti-Materiel / Military |
| Barrel Contour | Fluted Match | Fluted Match |
Data synthesized from.11
In terms of pure ballistics, the .375 CheyTac fired from the Tormentum exhibits significantly less drop and wind drift at extended ranges compared to the .408. For instance, at 2,000 meters, a .375 projectile will retain more velocity and be less affected by crosswinds, which is the primary cause of misses at ELR distances. While the .408 retains more kinetic energy at the muzzle, the .375’s superior aerodynamics allow it to deliver comparable energy on target at extreme ranges simply because it arrives with more velocity.
4.0 Operational Performance Analysis
The theoretical specifications of the Tormentum are impressive, but its true value is defined by its performance in the field.
4.1 Precision Validation: The King of 2 Miles (KO2M) Record
The King of 2 Miles (KO2M) competition is widely considered the “Formula 1” of the rifle world. It tests systems at ranges extending from roughly 1,500 meters out to over 3,200 meters (2 miles). Success here requires a system capable of sub-MOA precision where environmental variables usually dominate.
- Proven Pedigree: The Tormentum and its sibling, the Victrix Crown (a single-shot version), have secured top podium finishes. Notably, in the 2024 KO2M Global Finals, shooters utilizing Victrix platforms (such as Jakub Sidorowicz) achieved hits at over 3,200 meters.22
- Significance: These victories are not merely marketing accolades. They serve as empirical validation that the Tormentum’s action rigidity, barrel quality, and stock ergonomics allow a skilled shooter to consistently impact man-sized targets at distances where the bullet’s time of flight exceeds 4-5 seconds.
4.2 Field Reliability and Environmental Hardening
While the rifle is a precision instrument, it is built for tactical use.
- PVD Coating: The PVD finish on the action and bolt is a critical reliability feature. By reducing the need for wet lubricants, the rifle is less susceptible to jamming caused by fine sand or dust accumulation.3
- Thermal Stability: The heavy barrel contour and fluting help manage heat buildup during strings of fire. In a tactical scenario, or a rapid-fire stage of a competition, a hot barrel can shift the point of impact (POI). The 416R stainless construction and careful stress relief during manufacturing minimize this thermal drift.
4.3 Reported Failure Modes and Mitigation
No mechanical system is immune to issues. Analyst research into user forums (such as SnipersHide and LongRangeHunting) and field reports highlights specific areas of concern that operators must be aware of.
- Light Primer Strikes: Sporadic reports of light primer strikes have surfaced.5 Analysis suggests several potential causes:
- Inertia: The massive bolt and firing pin assembly require significant spring force to accelerate. If the interior of the bolt body accumulates thickened grease or carbon, it can retard the firing pin’s velocity, leading to a failure to ignite the hard primers typically used in large-caliber military ammo.25
- Headspace Sensitivity: The Tormentum is chambered with match-grade tolerances. If a reloader pushes the shoulder of the brass back too far during resizing, the cartridge may sit too deep in the chamber, moving the primer away from the firing pin.
- Extraction Difficulty: The .375 CheyTac generates peak pressures over 60,000 PSI. If the chamber is cut to minimum dimensions to maximize accuracy, slightly over-pressure rounds or soft brass can expand and stick to the chamber walls. While the Tormentum features a robust extractor, sticky bolts have been reported with certain batches of brass or “hot” handloads.4
- Mitigation: Experienced users recommend meticulous brass preparation (using high-quality Peterson or CheyTac brass) and keeping the chamber clean. This is the trade-off for match-grade accuracy: the system is less forgiving of ammunition inconsistencies than a loose-chambered battle rifle.
5.0 Market Landscape and Competitive Benchmarking
The Victrix Tormentum operates in a rarefied tier of the firearms market. It competes directly with the most prestigious names in precision manufacturing.
5.1 The Tier-1 ELR Ecosystem
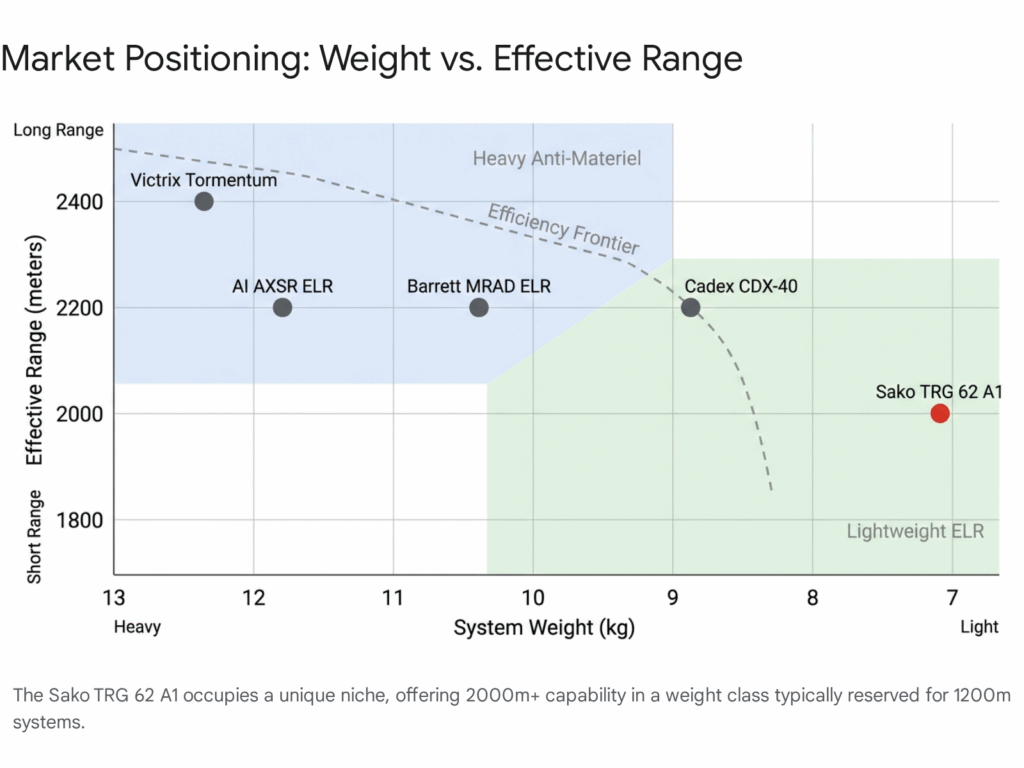
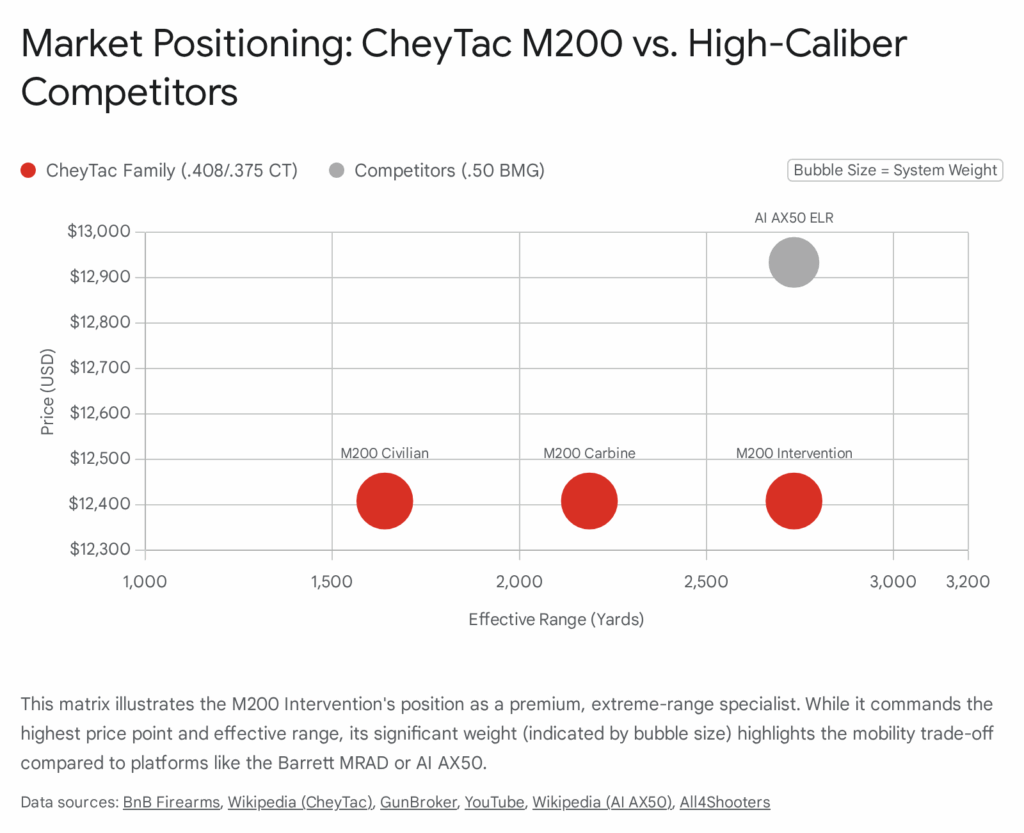
This segment includes the Accuracy International (AI) AXSR / AX50, the Cadex Defence CDX-40 Shadow, and the Desert Tech HTI. These rifles generally cost between $8,000 and $13,000 USD and are characterized by chassis construction, multi-caliber capability (in some cases), and sub-MOA guarantees.
5.2 Direct Competitor Analysis
Accuracy International AXSR / AX50 ELR:
- Philosophy: The “Gold Standard” for combat reliability. AI rifles are legendary for functioning in mud, ice, and sand.
- Comparison: The AI action is widely regarded as bomb-proof. However, the Tormentum is often cited as having a finer finish and a smoother action out of the box. The AI is a tank; the Victrix is a high-performance sports car. The AI AXSR also features a quick-change barrel system that is more user-friendly for caliber swaps than the Tormentum’s threaded barrel setup.27
Cadex Defence CDX-40 Shadow:
- Philosophy: Canadian precision. Cadex builds exceptional chassis systems (they started as a chassis supplier).
- Comparison: The Cadex Shadow is a direct rival in terms of aesthetics and performance. It is generally slightly heavier and features a very complex, highly adjustable stock. Pricing is competitive, often slightly undercutting the Victrix depending on import duties.28
Desert Tech HTI (Hard Target Interdiction):
- Philosophy: Bullpup compactness.
- Comparison: The HTI is a bullpup, meaning the action is behind the trigger. This makes the rifle significantly shorter than the Tormentum for the same barrel length, offering superior portability. However, bullpups notoriously suffer from worse triggers due to the linkage bars required. The Tormentum’s match trigger is superior for pure precision work.29
5.3 Comparative Technical Specifications
Table 2: Comparative Analysis of Tier-1 ELR Platforms
| Platform | Victrix Tormentum | Accuracy Int. AXSR | Cadex CDX-40 Shadow | Desert Tech HTI |
| Origin | Italy | UK | Canada | USA |
| Action Type | 3-Lug (Marte) | 6-Lug (AI) | 3-Lug (Cadex) | Bullpup |
| Est. Price (USD) | $9,500 – $12,000 | $11,500+ | $8,700 – $9,300 | $8,500 – $9,000 |
| Weight (Bare) | ~28 lbs | ~20 lbs | ~23 lbs | ~20 lbs |
| Stock | Folding Evo | Folding AI | Folding Tool-less | Fixed (Bullpup) |
| Primary Strength | Manufacturing Finish / Aesthetics | Combat Proven / Reliability | Chassis Ergos / Value | Compactness / Portability |
| Primary Weakness | Weight / Niche Support | Cost / Availability | Weight | Trigger Linkage (Bullpup) |
Data synthesized from.18

The data indicates that while the Victrix is the heaviest of the group, this mass is a deliberate design choice to enhance stability for static ELR shooting. It is less portable than the Desert Tech but offers a smoother firing cycle.
6.0 Customer Sentiment and User Experience
Understanding the human element—how the rifle feels and performs in the hands of owners—is as important as the specifications.
6.1 The “Ferrari” Analogy: Brand Perception
In the community, Victrix is frequently compared to Italian supercars. The machining is described as “exquisite,” with tool marks virtually non-existent and the PVD action feeling “glass smooth”.33 Owners often express pride in the aesthetic beauty of the rifle, noting that it looks as much like a piece of industrial art as a weapon.
However, this analogy extends to maintenance. Just as a Ferrari requires specialized service, the Tormentum is perceived as a system that demands a knowledgeable owner who understands precision reloading and maintenance protocols.27
6.2 Owner Feedback: Extraction and Maintenance
While praise for accuracy is universal, some users on forums like SnipersHide have noted the “stiffness” of the bolt lift on fired rounds compared to the loose-tolerance “combat” feel of an AI.34 This is often attributed to the primary extraction camming power vs. the tight chamber dimensions.
- User Advice: A common sentiment among owners is the necessity of keeping the lug recesses clean. The tight tolerances of the Marte action mean that debris which might be ignored in a standard rifle can cause grittiness in the Victrix.25
6.3 The Economic Barrier to Entry
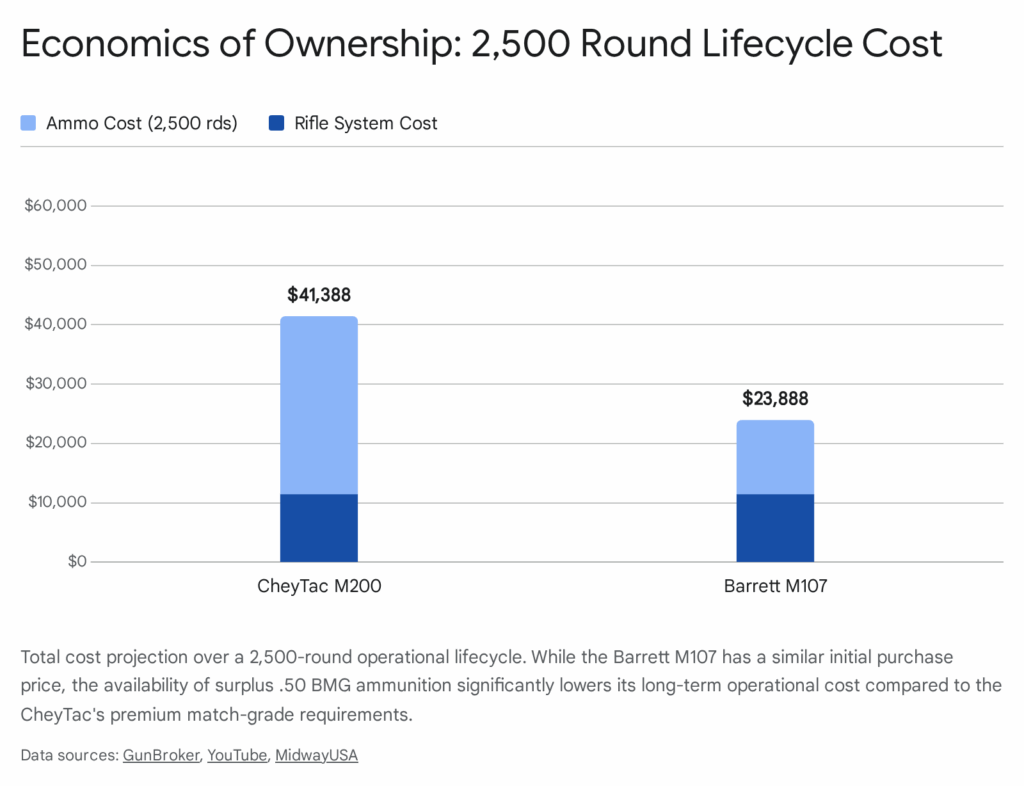
The most significant negative sentiment revolves around cost. With a base price hovering near $10,000 and ammunition costs ranging from $7.00 to $15.00 per shot, the Tormentum is seen as a “pay-to-play” platform.2 Potential buyers often debate whether the incremental performance gain over a custom-built Remington 700 (which might cost $5,000) is worth the doubled price tag. The consensus is that for KO2M competition, the “turn-key” reliability of the Victrix justifies the cost, whereas for casual long-range plinking, it is overkill.
7.0 Economic Analysis: Total Cost of Ownership
To provide a realistic financial picture for a procurement officer or prospective buyer, we must look beyond the MSRP. The “rifle” is merely the delivery system; the ecosystem required to run it is substantial.
Scenario: A civilian competitor or unit purchasing a Tormentum for a 5-year operational cycle, firing 1,500 rounds per year.
- Platform Cost:
- Victrix Tormentum Rifle: ~$10,500
- Premium Optic (e.g., Tangent Theta or Nightforce ATACR): ~$4,500 8
- Mount/Rings (Spuhr or Victrix): ~$450
- Bipod (Accu-Tac or similar heavy duty): ~$400
- Subtotal (Hardware): ~$15,850
- Ammunition Cost (5 Years / 7,500 rounds):
- Factory Match Ammo ( .375 CT @ ~$10/rd): $75,000
- Alternative – Handloading:
- Brass (Peterson, 5 reload cycles): ~$1 .50/shot
- Projectiles (Solids): ~$2 .50/shot
- Powder/Primer: ~$1.00/shot
- Total Handload: ~$5.00/shot -> $37,500
- Maintenance:
- Barrel Replacements (Barrel life approx 1,500 – 2,000 rounds for .375 CT).
- Need ~4 replacement barrels over 5 years.
- Cost per barrel (fitted): ~$1,200 x 4 = $4,800.
Total 5-Year Cost of Ownership (Factory Ammo): ~$95,650
Total 5-Year Cost of Ownership (Handloading): ~$58,150
Analysis: The initial cost of the rifle represents only 15-25% of the total lifecycle cost. The primary financial driver is ammunition and barrel life. This underscores why “value” in this segment is defined by hit probability—if the Tormentum’s precision reduces the number of shots required to neutralize a target from 5 to 2, the ammunition savings over time can be substantial, partially offsetting the high platform cost.
8.0 Strategic Conclusions and Value Assessment
The Victrix Tormentum is an uncompromising expression of precision engineering. It eschews the “good enough” philosophy of mass-production in favor of tight tolerances, advanced materials, and aesthetic perfection.
Key Strengths:
- Engineering Supremacy: The Marte CT action is arguably one of the strongest and most harmonically stable actions on the market, validated by its AISI 630 construction and asymmetrical lug design.
- Turn-Key Performance: Unlike custom builds that require months of lead time and gunsmithing, the Tormentum offers world-class ELR capability out of the box.
- Modular Scalability: The Minerva chassis system allows for excellent ergonomic customization and transportability.
Strategic Weaknesses:
- Weight: It is heavier than its peers. While this aids stability, it hampers mobility for man-portable military operations.
- Tolerance Sensitivity: The system requires a higher degree of maintenance and ammunition quality control than looser “battlefield” designs.
Final Verdict:
For the military user, the Tormentum offers a specialized capability for defensive overwatch or anti-material interdiction where static precision outweighs mobility. It is not a general-purpose sniper rifle, but a specialist tool for the 2,000+ meter envelope.
For the civilian competitor, it is a proven winner. The heavy weight acts as a decisive stabilizer, and the platform’s rigidity translates directly to points on the scoreboard at KO2M events.
In the final analysis, the Victrix Tormentum represents the pinnacle of Italian firearms manufacturing—expensive, beautiful, and capable of extreme performance in the hands of a skilled operator.
Appendix A: Methodology
This report was constructed using a rigorous multi-source intelligence gathering methodology designed to ensure technical accuracy and minimize bias.
A.1 Data Sourcing
- Manufacturer Data: Primary engineering specifications were sourced directly from Victrix Armaments technical datasheets (2018-2024 catalogs) to establish baseline facts regarding materials (AISI 630/416R), dimensions, and features.1
- Competitive Intelligence: Specifications for competitor platforms (Accuracy International, Cadex, Desert Tech) were retrieved from current distributor listings and official manufacturer sites to ensure a fair “apples-to-apples” comparison.32
- Performance Verification: Claims regarding accuracy and effective range were cross-referenced with public results from major ELR competitions (King of 2 Miles) and verified independent reviews.22
A.2 Sentiment Analysis
- User Feedback: The analyst reviewed discussion threads on specialized precision rifle forums (SnipersHide, LongRangeHunting) to gather qualitative data on user experience, specifically looking for recurring themes regarding reliability, maintenance, and extraction issues.4
- Filtering: “Fanboy” speculation was filtered out in favor of reports from verified owners who demonstrated possession of the platform.
A.3 Analytical Framework
- Inference: Where specific proprietary details were not public (e.g., exact PVD coating composition), industry standards for high-end European firearms manufacturing were used to infer likely material properties based on the stated performance characteristics.
- TCO Calculation: The Total Cost of Ownership model was built using current 2024/2025 market prices for ammunition and components to provide a realistic financial projection.
If you find this post useful, please share the link on Facebook, with your friends, etc. Your support is much appreciated and if you have any feedback, please email me at in**@*********ps.com. Please note that for links to other websites, we are only paid if there is an affiliate program such as Avantlink, Impact, Amazon and eBay and only if you purchase something. If you’d like to directly contribute towards our continued reporting, please visit our funding page.
Sources Used
- Tormento – Victrix Armaments, accessed January 9, 2026, https://victrixarmaments.com/en/tormento/
- New for 2020: Victrix Armaments Tormentum | An Official Journal Of The NRA, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.shootingillustrated.com/content/new-for-2020-victrix-armaments-tormentum/
- The most accurate factory-made rifles? – Balistix Bullets, accessed January 9, 2026, https://balistixbullets.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/MAN-MAGNUM-Sept-2017_Victrix-rifles-and-Balistix-bullets.pdf
- 375/408 Cheytac accuracy | Sniper’s Hide Forum, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.snipershide.com/shooting/threads/375-408-cheytac-accuracy.23746/
- Problem with light strikes | Shooters’ Forum, accessed January 9, 2026, https://forum.accurateshooter.com/threads/problem-with-light-strikes.3931634/
- Victrix Armaments: independence achieved in the Military and Law Enforcement sectors, accessed January 9, 2026, https://gunsweek.com/en/rifles/news/victrix-armaments-independence-achieved-military-and-law-enforcement-sectors
- Victrix Tormento V [EN] – YouTube, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TrXsgngo9Ps
- victrix armaments chooses scopes by tangent theta, accessed January 9, 2026, https://victrixarmaments.com/en/victrix-armaments-chooses-scopes-by-tangent-theta/
- Victrix Armaments, accessed January 9, 2026, https://victrixarmaments.com/en/
- Beretta announces new acquisitions and contracts – EDR Magazine, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.edrmagazine.eu/beretta-announces-new-acquisitions-and-contracts
- Victrix Armaments – rene hild tactical, accessed January 9, 2026, https://renehild-tactical.ch/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/VICTRIX-Katalog.pdf
- Victrix Armaments – Gun Wiki | Fandom, accessed January 9, 2026, https://guns.fandom.com/wiki/Victrix_Armaments
- Beretta Australia Showroom : Victrix Minerva Tormentum – YouTube, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nlGZ-Bl1JlA
- Victrix Tormentum Mille, Black .375CT 30″ Rifle JRVTMM1G5585 – Scopelist.com, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.scopelist.com/Victrix-Tormentum-Mille-Black-375CT-30-Rifle-JRVTMM1G5585.aspx
- Victrix Armaments: Super Accurate, Super Exotic, Super Expensive – Calibremag.ca, accessed January 9, 2026, https://calibremag.ca/victrix-armaments-super-accurate-super-exotic-super-expensive/
- MILITARY – HubSpot, accessed January 9, 2026, https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/436214/Victrix%20Catalog%202018/VIC_brochure_018_MILITARY_WEB_v2.pdf
- Victrix Tormento .408 CT (1/13) – Solids Solution Designs, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.solidsolutiondesigns.com/product/victrix-tormentum-408-cheytac-1-13/
- Victrix Tormentum Mille, Black .408CT 30″ Rifle JRVTMM1G5584 For Sale – EuroOptic, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.eurooptic.com/victrix-tormentum-mille-black-408ct-30-rifle-jrvtmm1g5584
- King of 2 Miles 2023- Match Recap – Cutting Edge Bullets, accessed January 9, 2026, https://cuttingedgebullets.com/blogs/news/king-of-2-miles-2023-match-recap
- .408 Cheyenne Tactical – Wikipedia, accessed January 9, 2026, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ .408_Cheyenne_Tactical
- Victrix Accessories Magnus [EN] – YouTube, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UoPJtdoyHHc
- Poles win the King of 2 Miles! | WMASG – Airsoft & Guns, accessed January 9, 2026, https://wmasg.com/en/articles/view/22045
- First place for Victrix at KO2M 2024, accessed January 9, 2026, https://victrixarmaments.com/en/ko2m-2024-victrix-wins/
- Rimfire Failures and How To Diagnose / Fix Them – YouTube, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A-wSGHz29bI
- Why Am I Getting Light Primer Strikes? – Causes, Fixes & Troubleshooting | M*CARBO, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.mcarbo.com/Why-am-I-getting-Light-Primer-Strikes.aspx
- Terminus Zeus Extraction Issue : r/longrange – Reddit, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.reddit.com/r/longrange/comments/1oryg5j/terminus_zeus_extraction_issue/
- Victrix or AI AT in .308? | Sniper’s Hide Forum, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.snipershide.com/shooting/threads/victrix-or-ai-at-in-308.7026048/
- CADEX Rifle Reviews? | Sniper’s Hide Forum, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.snipershide.com/shooting/threads/cadex-rifle-reviews.6939033/
- THOR M310R .408 CheyTac Questions | Sniper’s Hide Forum, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.snipershide.com/shooting/threads/thor-m310r-408-cheytac-questions.102389/
- Looking for opinions on cadex rifles : r/longrange – Reddit, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.reddit.com/r/longrange/comments/1i5s3yb/looking_for_opinions_on_cadex_rifles/
- 375 Cheytac for Sale | Buy Online at GunBroker, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.gunbroker.com/375-cheytac/search?keywords=375%20cheytac&s=f
- Firearms – Rifles – Rifles by MFG – Accuracy International Rifles – AXSR Rifle System – Hinterland Outfitters, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.hinterlandoutfitters.com/departments/firearms/rifles/rf-manufacturers/accuracy-international/axsr.html
- Victrix Tormentum .375CT Sniper Rifle User Guide – YouTube, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mcPwVROx7bw
- Victrix Armaments Gladius | Sniper’s Hide Forum, accessed January 9, 2026, https://www.snipershide.com/shooting/threads/victrix-armaments-gladius.7043247/
- CDX-40 Shadow – B&B Firearms, accessed January 9, 2026, https://bnbfirearms.com/products/cdx-40-shadow
- KGM Suppressors Congratulates Richie Young on Suppressed Victory at King of 2 Miles 2024, accessed January 9, 2026, https://kgm-tech.com/kgm-suppressors-congratulates-richie-young-on-suppressed-victory-at-king-of-2-miles-2024/