Published December 30, 2025. Revised January 16, 2025
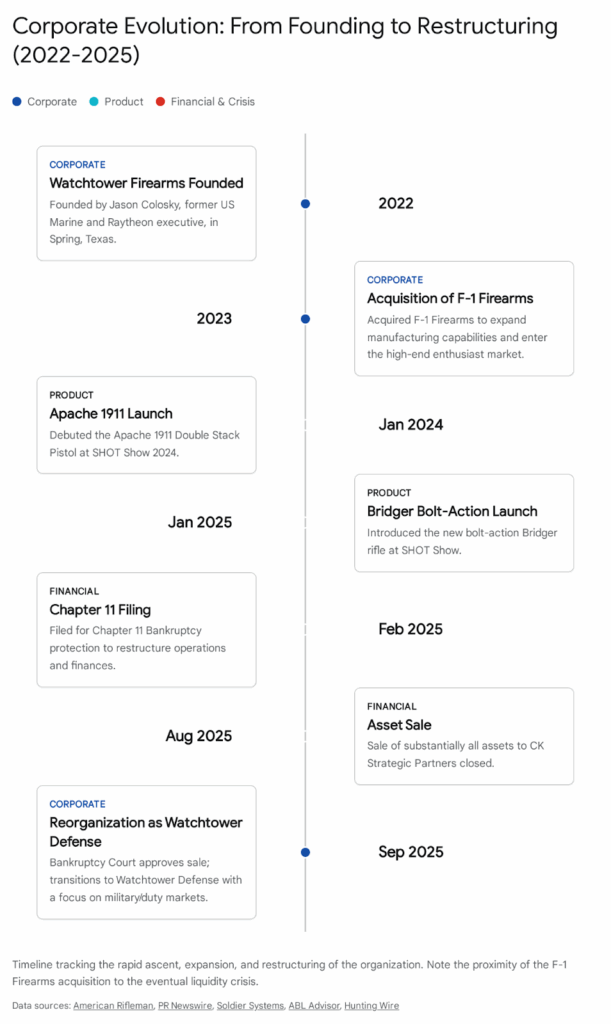
Watchtower Defense, operating initially as Watchtower Firearms, represents one of the most dynamic and volatile case studies in the post-pandemic American firearms industry. Established in 2022 by Jason Colosky, a former U.S. Marine and Raytheon executive, the company sought to disrupt the mid-market manufacturing sector by applying defense-industrial discipline to the commercial and law enforcement small arms markets. The company’s genesis was defined by the aggressive acquisition of F-1 Firearms in June 2023, a strategic move designed to secure immediate manufacturing capacity and precision machining infrastructure. However, the integration of a legacy “lifestyle” brand with a new “duty-focused” identity created significant operational and cultural friction.
The company rapidly gained visibility through a bifurcated market strategy: capitalizing on the booming “2011” double-stack pistol market through high-profile influencer collaborations—most notably with Demolition Ranch and PewView—while simultaneously pursuing institutional legitimacy through law enforcement contracts for its Type 15 rifle platform. This rapid expansion, however, collided with the harsh realities of capital-intensive manufacturing. By late 2024, the company faced a liquidity crisis exacerbated by supply chain bottlenecks, an escalating backlog of pre-orders, and severe legal disputes with landlords and minority shareholders. These pressures culminated in a Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing in February 2025, a move leadership characterized as a strategic reorganization but which bore the hallmarks of a necessary intervention to prevent insolvency.
Through a complex restructuring process supported by Debtor-in-Possession (DIP) financing, the company’s assets were acquired in a Section 363 sale by CK Strategic Partners in late 2025. Emerging as “Watchtower Defense,” the new entity has shed significant liabilities and legacy disputes, relocating to a new 24,000-square-foot facility in Spring, Texas. The reorganized company now faces the dual challenge of rehabilitating its reputation with the commercial consumer base while executing a strategic pivot toward defense and federal contracting. This report provides an exhaustive analysis of the company’s history, product evolution, financial restructuring, and strategic outlook as it enters the 2026 fiscal year.
1. Introduction: The Strategic Landscape of the Post-2020 Firearms Market
To fully appreciate the trajectory of Watchtower Defense, it is essential to first establish the macroeconomic and industry-specific context into which the company was born. The American firearms industry in 2022 was in a state of complex transition, recovering from the historic demand surge of 2020–2021 while facing new headwinds in supply chain management and consumer preference shifts.
1.1 The Post-Surge Normalization
The years 2020 and 2021 witnessed an unprecedented spike in firearms sales, driven by the COVID-19 pandemic, social unrest, and political uncertainty. During this period, manufacturers maximized throughput, often sacrificing product diversity for raw volume. By 2022, however, the market had entered a period of “normalization.” The entry-level AR-15 market, which had been the primary engine of growth, became saturated with inventory. Prices for standard “commodity” rifles plummeted, squeezing margins for manufacturers who competed solely on price.
In contrast, the market for premium, specialized firearms remained robust. The “high-end” consumer—often an enthusiast with multiple firearms—continued to spend discretionary income on differentiated products. This bifurcation created a specific opportunity: a manufacturer that could offer perceived bespoke quality at a scalable production volume could capture the high-margin segment that mass-market producers were neglecting.
1.2 The Rise of the “2011” Platform
Concurrently, 2022 marked the mainstream explosion of the “2011” platform—a modernized, double-stack variation of the classic 1911 pistol design. Historically the domain of custom gunsmiths and competitive shooters, the 2011 began to cross over into the tactical and duty markets, led by brands like Staccato (formerly STI). Law enforcement agencies began approving these platforms for duty use, signaling a paradigm shift away from the polymer-striker-fired dominance of Glock and Sig Sauer.
This trend created a vacuum for new entrants. While Staccato dominated the duty sector and Atlas Gunworks commanded the ultra-premium competition sector, there was a perceivable gap for a brand that could merge the “tactical” aesthetic with the “race gun” performance, marketed aggressively to a younger, digital-native demographic. This was the specific market environment Jason Colosky identified when formulating the business case for what would become Watchtower Firearms.1
1.3 The Defense-Industrial Thesis
Against this backdrop, the founding thesis of Watchtower was distinct. Most firearms companies are founded by gunsmiths, competitive shooters, or marketing professionals. Jason Colosky, however, brought a background from the “Defense Prime” sector. As a former executive at Raytheon overseeing strategic engagements with the Pentagon and the White House, Colosky possessed an understanding of the military-industrial complex that is rare in the small arms commercial market.3
His vision was to build a “Raytheon for small arms”—a company that utilized the rigorous systems engineering, quality assurance, and contracting discipline of a major defense contractor but applied it to a nimble manufacturing base. The goal was to bridge the divide between “commercial spec” (often focused on aesthetics and price) and “mil-spec” (focused on reliability and interchangeability), creating a product line that could seamlessly transition between a civilian’s range bag and a SWAT officer’s patrol rifle.4
2. The Genesis of Watchtower (2022–2023)
The corporate history of Watchtower is characterized by speed. Unlike legacy manufacturers that grew organically over decades, Watchtower was engineered for rapid scaling from day one.
2.1 Founding Philosophy and Branding
Watchtower Firearms was incorporated in 2022 in Spring, Texas.5 The name selection was deliberate and deeply rooted in military heritage. “Operation Watchtower” was the code name for the Guadalcanal campaign in World War II, a pivotal offensive where U.S. Marines fought under grueling conditions.3 By adopting this moniker, the company signaled its intended identity: American, expeditionary, and resilient.
This branding was not merely cosmetic; it was a core component of the company’s value proposition. In an industry saturated with “tactical” brands, establishing a credible lineage to military service—reinforced by Colosky’s own background as a Recon Marine—was essential for building trust with the law enforcement community.3 The marketing narrative emphasized that while competitors might “take shortcuts and outsource,” Watchtower would “command the high ground” through domestic manufacturing and precision engineering.3
2.2 The Acquisition of F-1 Firearms
The most critical strategic maneuver in the company’s early history was the acquisition of F-1 Firearms on June 12, 2023.7 F-1 Firearms was a well-known entity in the Texas firearms manufacturing hub. For a decade, F-1 had carved out a niche producing highly stylized, “skeletonized” AR-15s—rifles with material machined away from the receiver and handguard to reduce weight and reveal the internal components.5
For Colosky and his investors, F-1 represented a “turnkey” manufacturing solution. Building a firearms factory from the ground up requires navigating complex ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) compliance, ATF licensing, machine tool procurement, and skilled labor hiring—a process that can take years. F-1 already possessed:
- Precision Machining Capacity: High-end CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines capable of intricate milling.4
- Skilled Workforce: A team experienced in operating these machines and assembling AR-platform rifles.
- Existing Distribution: A network of dealers and distributors already familiar with the entity.
However, the acquisition presented a substantial brand identity challenge. F-1 Firearms was known for “gamer guns”—flashy, colorful, and skeletonized rifles that were popular on Instagram but generally regarded as unsuitable for duty use due to the potential for debris ingress. Watchtower’s mission was to build serious tools for professionals. The challenge, therefore, was to utilize F-1’s precision capability (which Colosky noted had “miniscule waste” and high efficiency) to produce a completely different class of product.4
The acquisition was a classic “platform” play: buy the capability, retire the legacy brand identity over time, and pivot the output to a new, higher-value segment. This transition, however, would prove to be operationally difficult, as legacy orders for F-1 products had to be fulfilled even as the new Watchtower product lines were being developed.9
3. Product Architecture and Market Segmentation
Watchtower’s product strategy was designed to attack the “premium” segment of the market on two fronts: the emerging “2011” pistol market and the “duty-grade” rifle market. This dual-track approach allowed them to capture revenue from high-net-worth civilian enthusiasts while building the portfolio necessary for government contracting.
3.1 The Apache 1911 Double-Stack Program
The flagship of the Watchtower brand, and the primary driver of its 2024 visibility, was the Apache 1911 Double-Stack pistol. Launched at SHOT Show 2024, the Apache was an ambitious entry into a market dominated by entrenched players.1
3.1.1 Engineering and Design Philosophy
The Apache was not a clone; it was an engineered attempt to optimize the 2011 platform for manufacturing at scale.
- Material Selection: The frame was constructed from pre-hardened 4140 stainless steel, while the slide utilized 416R stainless steel. This choice of materials prioritized durability and corrosion resistance, essential for the “duty” designation the company sought.10
- Integrated Compensation: A key feature of the Apache line was the integration of recoil compensation systems. The “PewView” edition, for instance, featured a ported barrel and slide design that directed expanding gases upward to counteract muzzle rise.10 This is a feature highly prized in competitive shooting for reducing “split times” (the time between shots).
- Surface Treatment: Watchtower utilized a proprietary PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating. PVD offers superior lubricity and hardness compared to traditional Cerakote, reducing the need for lubrication and increasing the lifespan of moving parts. This was a direct selling point against competitors using standard finishes.12
3.1.2 The “Race Gun” for Duty Use
The marketing positioning of the Apache was unique. While engineered with the tolerances of a competition “race gun,” it was marketed as a tool for the “American warrior”.13 This hybrid positioning attempted to broaden the Total Addressable Market (TAM) to include both USPSA/IDPA competitors and tactical enthusiasts who wanted a “battle-ready” double-stack 1911. Pricing the unit in the $3,000 to $4,000 range placed it directly in competition with Staccato’s XC and Atlas Gunworks’ lower-tier offerings.11
3.2 The Type 15 Rifle Series: The F-1 Evolution
While the Apache captured the headlines, the Type 15 rifle series represented the company’s core manufacturing capability. The Type 15 was the direct evolution of the F-1 Firearms lineage, but “de-skeletonized” for professional use.
3.2.1 From Skeleton to Spec-Ops
The transition from F-1’s “skeletonized” receivers to Watchtower’s “Spec Ops” Type 15 was a critical branding pivot. Professional end-users (police and military) generally reject skeletonized rifles because open receivers allow dirt, mud, and debris to enter the action, inducing malfunctions. Watchtower’s Type 15 featured closed receivers with tight tolerances—so tight, according to Colosky, that “you could shake it and it wouldn’t make a sound”.4
- The Durabolt BCG: The rifle featured a proprietary “Durabolt” Bolt Carrier Group (BCG) with a Tru-Black PVD coating. The BCG is the heart of the AR-15 platform; by focusing on the metallurgy and finish of this component, Watchtower emphasized reliability and ease of cleaning.14
- Law Enforcement Validation: The most significant milestone for the Type 15 program was the contract with the Lafayette, Louisiana Police Department. The department purchased 118 Type 15M rifles in March 2025.5
- Analyst Insight: For a new manufacturer, a departmental contract is worth far more than the revenue it generates. It serves as a “stamp of approval.” Police departments typically conduct distinct Testing & Evaluation (T&E) phases involving round counts, drop tests, and adverse condition tests. Winning this contract signaled to other agencies that the Type 15 was not just a rebranded hobbyist rifle but a validated duty weapon.
3.3 The Bridger Bolt-Action: Diversification
In January 2025, amidst its financial restructuring, Watchtower introduced the “Bridger” bolt-action rifle at SHOT Show.5 This marked a diversification into the precision hunting and long-range shooting market.
- Strategic Rationale: The bolt-action market has seen a resurgence due to the popularity of the PRS (Precision Rifle Series) and long-range hunting. By entering this space, Watchtower attempted to reduce its reliance on the politically volatile AR-15 market and tap into the “crossover” hunter demographic. It also utilized the same precision machining capabilities required for the 1911 and AR platforms, maximizing machine utilization rates.
4. Market Strategy: The Influencer-Industrial Complex
Watchtower’s rapid ascent in brand awareness can be attributed to its aggressive use of what industry analysts term the “Influencer-Industrial Complex.” In the firearms industry, traditional advertising channels (Facebook, Google, TV) are largely restricted. Consequently, manufacturers rely heavily on YouTube personalities and social media influencers to drive sales. Watchtower did not just use influencers for marketing; it integrated them into product development.
4.1 The Demolition Ranch Partnership
The collaboration with Matt Carriker, creator of “Demolition Ranch” (one of the largest firearms channels on YouTube), was a defining moment for the brand. The partnership resulted in the “Demolitia” 1911, a limited-edition pistol built to Carriker’s specifications.17
- The “Drop” Model: Watchtower utilized a “drop culture” sales model, similar to streetwear brands like Supreme. They offered limited VIP packages (the first 500 units) that included exclusive morale patches and hats. This created artificial scarcity and a sense of urgency, driving a massive influx of pre-orders.17
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Power: This strategy allowed Watchtower to capture high-margin direct sales, bypassing the thinner margins associated with distribution through wholesalers. However, it also created a direct accountability loop with the customer base.
4.2 The PewView Collaboration
Similarly, the partnership with Nick “PewView” Johnson targeted the “tactical performance” demographic. PewView is known for high-speed, trick-shooting content that emphasizes the visual aesthetic of shooting (e.g., muzzle flash, recoil control).
- Product Fit: The “PewView Limited Edition” Apache was designed specifically for this style of shooting, featuring the integrated compensator to flatten recoil for video-worthy rapid fire.10
- Validity by Association: By associating the brand with a shooter known for extreme skill, Watchtower implicitly validated the performance of the firearm. If PewView could run the gun fast, the implication was that the gun was capable of elite performance.
4.3 Risks of the Influencer Model
While highly effective for generating initial revenue, this model introduced significant risk.
- Supply Chain Strain: The viral nature of influencer marketing can generate demand spikes that overwhelm manufacturing capacity. Watchtower faced precisely this issue, leading to backlogs and consumer frustration.16
- Reputational Tying: The brand’s reputation became inextricably linked to the influencers. Any delay in shipping wasn’t just a Watchtower failure; it was perceived as a failure of the influencer’s promise, leading to distinct pressure from the partners to fulfill orders.
- The “Pre-Order” Trap: Relying on pre-orders for cash flow can be dangerous. If the capital from pre-orders is used for operational expenses (OpEx) rather than materials (COGS), a company can find itself in a “Ponzi-like” fulfillment cycle where new sales are needed to fund the production of old orders. While there is no direct evidence of malfeasance, the liquidity crisis of late 2024 suggests the company struggled to balance the capital inflows from these drops with the high costs of scaling production.
5. Operational Distress and The Liquidity Crisis (2024–2025)
By late 2024, the disconnect between Watchtower’s aggressive marketing promises and its operational reality began to widen. The rapid scaling following the F-1 acquisition exposed fragility in the company’s capital structure and supply chain.
5.1 The Manufacturing Bottleneck
Transitioning a factory from making skeletonized AR-15 parts (which are relatively tolerant of dimensional variance) to fitting tight-tolerance double-stack 1911s is a non-trivial engineering challenge. The 2011 platform is notoriously difficult to manufacture; unlike polymer pistols, it requires significant hand-fitting or ultra-precise machining to function reliably.
- The Backlog: Reports from consumer forums indicated that customers were experiencing significant delays in receiving their Apache and Demolitia pistols.16 In the era of social media, this negative sentiment spread quickly, countering the positive narrative driven by the influencers.
- Quality Control (QC) Pressures: The pressure to clear the backlog created risks of QC slippage. Industry observers noted that rapid scaling of 2011 production often leads to reliability issues if the “tuning” process is rushed.
5.2 The Landlord and Shareholder Disputes
Behind the scenes, the corporate structure was fracturing. The acquisition of F-1 Firearms had involved retaining the original founders (the Podgurnys) as minority stakeholders and utilizing their existing facility. This arrangement collapsed into litigation.
- Lease Disputes: Watchtower became embroiled in a conflict with the landlord of its Spring, Texas facility. While the landlord alleged ‘serious lease breaches’ and obtained an eviction order in December 2024, Watchtower remained in possession of the facility until November 2025. Notably, the company claimed ‘record production’ levels in July 2025, suggesting that internal liquidity constraints, rather than physical displacement by the landlord, were the primary driver of distress.
- Shareholder Litigation: In July 2025, F-1 Firearms, LLC (the entity representing the sellers) filed a lawsuit against Jason Colosky and Watchtower in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Texas.20 The nature of the suit, involving securities statutes, suggests a breakdown in the post-acquisition agreement—likely related to earn-out payments, valuation adjustments, or allegations of how the new management was running the acquired assets.
5.3 Personnel Turnover
The internal turmoil was reflected in leadership changes. Ray Care, a former Navy SEAL who served as the “Chief Culture Officer” and a public face of the brand alongside Colosky, departed the company during this period.21 Community discussions suggest this departure was involuntary and acrimonious, further indicating a struggle for control over the company’s direction and resources.
6. The Collapse: Chapter 11 Reorganization (2025)
“The convergence of operational bottlenecks, mounting legal costs resulting from extensive self-initiated litigation against vendors and legacy stakeholders, and a tightening of liquidity forced Watchtower’s hand.
6.1 The “Strategic” Bankruptcy Narrative
CEO Jason Colosky publicly framed the filing as a “strategic move” designed to “streamline internal operations and finances” while the firm continued to grow.5
- Interpretation: In corporate restructuring terms, this framing is standard for preserving customer confidence. A “strategic” bankruptcy implies the core business model is sound, but the balance sheet needs cleansing.
- Defensive Utility: The Chapter 11 filing triggered an “automatic stay,” immediately halting the lawsuits from the landlord and the F-1 sellers. This bought the company crucial time to find a financial solution without the immediate threat of eviction or asset seizure.
6.2 Debtor-in-Possession (DIP) Financing
To survive the bankruptcy process, a company needs cash to pay employees and buy materials. In June 2025, the court approved Debtor-in-Possession (DIP) financing for Watchtower.15
- The Lender: The financing was provided by CK Strategic Partners, an investment entity that would ultimately play the decisive role in the company’s future.
- Operational Continuity: While financing allowed Watchtower to continue fulfilling orders during the bankruptcy proceedings, financial filings reveal the company incurred operating losses totaling approximately $4.6 million between March and August 2025. This indicates that while revenue streams existed, the company continued to struggle with significant burn rates throughout the restructuring.
7. The Restructuring Mechanism: Section 363 Sale
The resolution of Watchtower’s crisis was not a reorganization of the existing debt, but a sale of the underlying assets. This was executed via a Section 363 sale under the Bankruptcy Code, a powerful tool that allows assets to be sold “free and clear” of liens and liabilities.
7.1 The “Loan-to-Own” Strategy
The buyer was CK Strategic Partners, the same entity that provided the DIP financing.9 This transaction structure typically follows a specific pattern:
- The lender provides emergency funding (DIP) secured by a super-priority lien on all assets.
- When the company cannot repay the loan, the lender uses the debt they are owed to “credit bid” for the company’s assets at auction.
- The lender acquires the business (assets, brand, IP) without taking on the toxic liabilities (lawsuits, unsecured debt, bad leases).
In August 2025, the court approved the sale. CK Strategic Partners acquired “substantially all assets” of Watchtower Firearms, LLC.9
7.2 The Result: Watchtower Defense
The closing of the transaction in September 2025 marked the end of “Watchtower Firearms, LLC” as the operating entity and the birth of Watchtower Defense.23
- Liability Segregation: The old disputes—the lease arrears, the F-1 shareholder litigation—likely remained with the “old” corporate shell (the bankruptcy estate), which would be liquidated to pay creditors cents on the dollar.
- The Clean Slate: The new entity, Watchtower Defense, emerged with the machinery, the intellectual property (IP) for the Apache and Type 15, the brand trademarks, and the key personnel, but with a cleansed balance sheet ready for capitalization.

8. The New Era: Watchtower Defense (Late 2025)
As of December 2025, Watchtower Defense operates as a reorganized entity with a refined strategic focus. The rebranding from “Firearms” to “Defense” is not accidental; it reflects a deliberate pivot toward the B2G (Business-to-Government) sector, aligning with Colosky’s original vision.
8.1 Infrastructure Relocation
One of the first major initiatives of the new ownership was to announce the development of a new 24,000-square-foot manufacturing facility in Spring, Texas.24
- Operational Rationale: This facility allows the company to physically exit the site associated with the landlord dispute. More importantly, it provides the footprint to install modern manufacturing cells designed for “one-piece flow,” a lean manufacturing technique critical for reducing the work-in-progress (WIP) inventory that plagued the F-1 facility.
- Capacity Expansion: The investment in “state-of-the-art production” machinery suggests that CK Strategic Partners is committed to capital expenditure (CapEx) to solve the throughput bottlenecks that led to the consumer backlog.22
8.2 Leadership Continuity and Governance
Despite the turmoil, Jason Colosky retained his position as CEO.3 This is notable; often in Section 363 sales, management is replaced. His retention suggests that the acquiring group—comprised of a prior insider investor acting as a stalking-horse bidder—opted to maintain continuity. The transaction, valued at a $900,000 bid, primarily altered vendor obligations rather than injecting material new operating capital, indicating a consolidation of control rather than an arm’s-length institutional bailout.
- Professionalization: The departure of “culture” figures like Ray Care and the retention of operational veterans like Graham Kohlmeyer (COO, ex-Beretta) indicates a shift toward professional corporate governance.3 The company is moving away from a personality-driven culture toward an operations-driven culture.
- Advisory Board: While former Sheriff Mark Lamb previously served on the advisory board, he was removed from the company website in early 2025, signaling a shift in the company’s governance structure.
8.3 The “Duty-Focused” Mandate
The press releases following the acquisition emphasize a “duty-focused product line”.23 While the company continues to sell the Apache and Demolitia to civilians (indeed, clearing the backlog is a priority), the strategic language has shifted. The future growth engine is viewed as defense and law enforcement sales.
- Why Defense? Government contracts are “sticky.” Once a department adopts a platform, they buy spare parts, training, and replacements for years. This provides predictable, long-term revenue that balances the volatility of the consumer market.
9. Strategic Outlook (2026–2030)
Looking ahead to 2026 and beyond, Watchtower Defense faces a critical rehabilitation period. The brand possesses high-value IP and a strong aesthetic identity, but it must overcome the “trust deficit” created by the 2024 delays and bankruptcy news.
9.1 The Path to Recovery
- Consumer Rehabilitation: The immediate priority is fulfilling all pre-bankruptcy backorders. The company has stated that production is now “running at its highest level”.13 Successfully delivering these units is the only way to silence the negative sentiment on enthusiast forums.
- The “Bridger” Launch: Successfully bringing the bolt-action rifle to market will demonstrate that the company is capable of R&D and launching new products even while restructuring.
- Tier 2 Contracts: Watchtower is likely to target “Tier 2” law enforcement agencies—mid-sized departments (like Lafayette PD) that are large enough to offer a valuable contract but small enough to be flexible in their procurement, unlike federal agencies that are locked into multi-year contracts with giants like Sig Sauer or Glock.
9.2 The GovCon Opportunity
With Colosky’s background, the long-term play is almost certainly Federal and Foreign Military Sales (FMS).
- FMS Potential: The “Raytheon connection” is most valuable in the export market. U.S. allies in Eastern Europe and Southeast Asia are re-arming. A “Made in USA” rifle with a military lineage, marketed by a CEO who speaks the language of the State Department, has a distinct competitive advantage in these boutique export markets.
9.3 Risks and Challenges
- Capital Requirements: Defense manufacturing is capital intensive. The new facility will require millions in tooling. CK Strategic Partners must have the patience to fund this ramp-up before the defense contracts start paying out.
- Market Saturation: The 2011 market is becoming crowded. New entrants (Springfield Armory, Kimber, etc.) are entering the space at lower price points. Watchtower must defend its premium pricing through superior brand equity and performance.
10. Conclusion
Watchtower Defense is a company reborn. Its initial iteration—Watchtower Firearms—was a bold but structurally flawed attempt to merge a legacy “lifestyle” manufacturer with a “mil-spec” vision, fueled by the volatile propellant of influencer marketing. The resulting explosion generated massive visibility but shattered the company’s operational and financial containment vessels.
The restructuring of 2025 was a necessary evolution. By shedding the liabilities incurred following the 2023 asset acquisition through the Section 363 sale, and by utilizing the credit bid backing of CK Strategic Partners, Watchtower Defense has attempted to secure a second chance.”
The future of Watchtower depends on execution. If the new facility in Spring, Texas, can deliver the promised “Spec Ops” quality at scale, and if the leadership can leverage its defense-industrial DNA to secure government contracts, Watchtower Defense is well-positioned to become a significant player in the American small arms industry. The “Raytheon of small arms” vision remains viable, but the company has learned the hard way that in manufacturing, logistics eats strategy for breakfast.
Appendix: Summary of Key Milestones
| Year | Milestone Event | Description | Strategic Impact |
| 2022 | Founding | Jason Colosky founds Watchtower Firearms in Spring, Texas. | Established the “Operation Watchtower” military heritage brand identity. |
| 2023 | F-1 Acquisition | Watchtower acquires F-1 Firearms (June 12). | Secured immediate manufacturing capacity but inherited legacy “lifestyle” brand baggage. |
| 2024 | Apache Launch | Launch of the Apache 1911 Double Stack at SHOT Show. | Marked entry into the premium “2011” market; utilized influencer partnerships (PewView). |
| 2024 | Demolition Ranch | Partnership with Matt Carriker for “Demolitia” pistol. | Generated massive pre-order volume but strained supply chain and fulfillment. |
| 2024 | Liquidity Crisis | Operational backlogs and landlord disputes intensify. | Consumer sentiment sours due to delays; legal pressure mounts from legacy stakeholders. |
| 2025 | Bankruptcy Filing | Filed Chapter 11 Bankruptcy (February). | “Strategic” filing to halt litigation and restructure debt; operations continued. |
| 2025 | LE Validation | Lafayette PD (LA) receives shipment of Type 15M rifles. | Critical “proof of life” during bankruptcy; validated the product for duty use. |
| 2025 | DIP Financing | Court approves financing from CK Strategic Partners (June). | Provided liquidity to maintain staff and production during the restructuring. |
| 2025 | Asset Sale | Section 363 sale to CK Strategic Partners closes (Aug/Sept). | Separated assets from toxic liabilities; ownership transferred to lender group. |
| 2025 | Rebranding | Re-launched as Watchtower Defense. | Corporate pivot to “Defense” identity; announcement of new 24k sq ft facility in Spring, TX. |
Works cited
- WATCHTOWER Firearms Unveils the APACHE 1911 Double-Stack Pistol: A New Era in 1911’s | Soldier Systems Daily, accessed December 27, 2025, https://soldiersystems.net/2024/01/18/watchtower-firearms-unveils-the-apache-1911-double-stack-pistol-a-new-era-in-1911s/
- The NEW Watchtower Apache Double Stack 1911 [TriggrCon 2023] : r/2011 – Reddit, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.reddit.com/r/2011/comments/16thupf/the_new_watchtower_apache_double_stack_1911/
- Our Story – Watchtower Firearms, accessed December 27, 2025, https://watchtowerfirearms.com/our-story/
- FYI – Watchtower on The Move – SHOT Business, accessed December 27, 2025, https://shotbusiness.com/2024/05/columns/fyi-watchtower-on-the-move/
- Watchtower Firearms Re-Organizing | An Official Journal Of The NRA – American Rifleman, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.americanrifleman.org/content/watchtower-firearms-re-organizing/
- HeadHunters NW Video Podcast: Origins of Watchtower Firearms | Outdoor Wire, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.theoutdoorwire.com/releases/1ce2ff9e-c129-44dd-a522-2aa0d439379c
- Watchtower Firearms Acquires F-1 Firearms | Mergr M&A Deal Summary, accessed December 27, 2025, https://mergr.com/transaction/watchtower-firearms-acquires-f-1-firearms
- WATCHTOWER Announces the Acquisition of F-1 Firearms, LLC and Launches with Fanfare to Redefine the Firearm Industry – PR Newswire, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/watchtower-announces-the-acquisition-of-f-1-firearms-llc-and-launches-with-fanfare-to-redefine-the-firearm-industry-301847589.html
- SSG Advises Watchtower Firearms in Sale to CK Strategic Partners – News | ABL Advisor, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.abladvisor.com/news/41487/ssg-advises-watchtower-firearms-in-sale-to-ck-strategic-partners
- WATCHTOWER APACHE PEW VIEW LIMITED EDITION DOUBLE STACKED 1911, 4.6″ 9MM w/ COMP, 1-17RD, 1-21RD MAG, PISTOL **USED LIKE NEW – BattleHawk Armory, accessed December 27, 2025, https://battlehawkarmory.com/product/watchtower-apache-pew-view-limited-edition-double-stacked-1911-4.6-9mm-w-comp-1-17rd-1-21rd-mag-pistol
- Watchtower Firearms, Demolition Ranch Team Up For Limited-Edition DEMOLITIA Blackout 1911 | An NRA Shooting Sports Journal, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.ssusa.org/content/watchtower-firearms-demolition-ranch-team-up-for-limited-edition-demolitia-blackout-1911/
- Watchtower Firearms: A Premium American Company to Watch – Guns and Ammo, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.gunsandammo.com/editorial/watchtower-firearms-a-premium-american-company-to-watch/490886
- WATCHTOWER Firearms Hits Highest Production Level Since Inception – Outdoor Wire, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.theoutdoorwire.com/releases/d148874d-84f8-4bd8-8606-dbba145f0b70
- WATCHTOWER SPEC OPS Type 15 Rifle in .223 Wylde – RifleShooter, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.rifleshootermag.com/editorial/watchtower-spec-ops-type-15-rifle-in-223-wylde/490505
- Court Approves Watchtower Firearms DIP Financing | An Official Journal Of The NRA, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.americanrifleman.org/content/court-approves-watchtower-firearms-dip-financing/
- Watchtower Firearms Reorganizes, But It’s Still In Business | thefirearmblog.com, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.thefirearmblog.com/blog/watchtower-firearms-reorganizes-but-it-s-still-in-business-44820586
- WATCHTOWER Introduces Limited Edition DEMOLITIA – 1911 Double Stack 9mm | Soldier Systems Daily, accessed December 27, 2025, https://soldiersystems.net/2024/10/10/watchtower-introduces-limited-edition-demolitia-1911-double-stack-9mm/
- As expected Watchtower Firearms are on their way out : r/2011 – Reddit, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.reddit.com/r/2011/comments/1j08cbe/as_expected_watchtower_firearms_are_on_their_way/
- Texas gunmaker announces new strategy after bankruptcy – Chron, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.chron.com/culture/article/watchtower-firearms-texas-21078416.php
- F-1 Firearms, LLC et al v. Colosky et al 4:2025cv03108 – Justia Dockets, accessed December 27, 2025, https://dockets.justia.com/docket/texas/txsdce/4:2025cv03108/2017003
- Watchtower Firearms Now Up For Asset Sale, Liquidation or Auction : r/2011 – Reddit, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.reddit.com/r/2011/comments/1l9prno/watchtower_firearms_now_up_for_asset_sale/
- Watchtower Defense acquires substantially all assets of Watchtower Firearms, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.guntradeworld.com/watchtower-defense-acquires-substantially-all-assets-watchtower-firearms
- WATCHTOWER Defense Acquires WATCHTOWER Firearms’ Assets in Court-Approved Chapter 11 Sale – Hunting Wire, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.huntingwire.com/releases/06eafa44-482a-4e76-997c-3fc0edbeac4e
- WATCHTOWER Defense and Its Owners Acquire Substantially All the Assets of WATCHTOWER Firearms | Outdoor Wire, accessed December 27, 2025, https://www.theoutdoorwire.com/releases/dafdf8a6-79b2-4b4b-a5a0-64da3c39c2ea
- Newsmakers – April 2025 – Shooting Industry Magazine, accessed December 27, 2025, https://shootingindustry.com/industry-news/new-hires/newsmakers-april-2025/